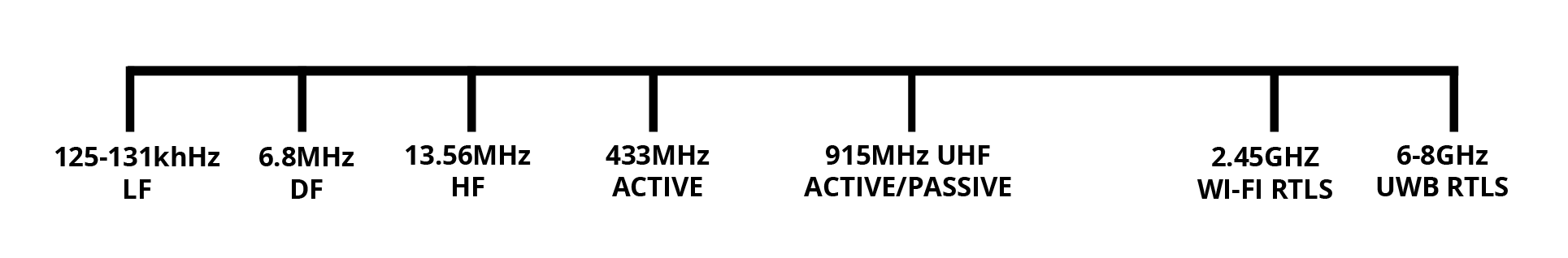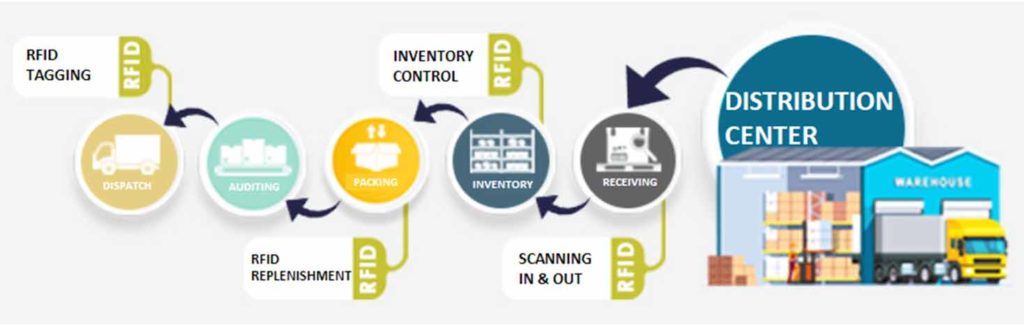

In the warehousing industry, anything that facilitates the organization and management of your inventory is a huge advantage. Things have come a long way since the pen and paper days, but maintaining an accurate and up-to-date picture of your entire operation can still be a challenge. (Remember, we have millions of square feet of storage to keep tabs on.) Luckily, RFID technology has entered the scene. With its power to decrease human error and streamline warehouse operations, RFID has become one of the most important implements the supply chain manager’s toolbox.